
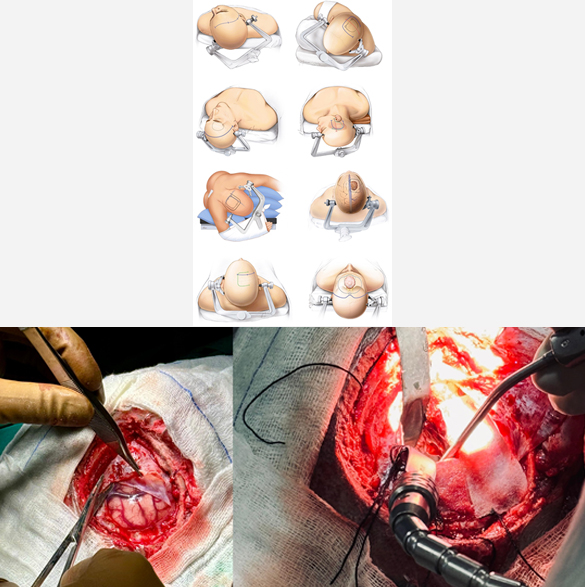
Brain Tumor Surgery
Most of the brain tumors are treated with surgery first. They may need additional treatment with radiotherapy, chemotherapy or hormonal therapy. Brain tumor surgery is a specialized and delicate procedure, requiring good preoperative and postoperative management. Brain tumor surgery generally requires opening the cranium/skull (craniotomy) and tumor removal (excision). Surgical excision can be; gross total resection (GTR), maximum safe resection (MSR), partial resection, decompression, biopsy. The outcome of brain tumor surgery depends on the site, size and type of the tumor inside the brain. Few complications of the brain tumor surgery may be wound infection, intracranial bleeding, seizures, meningitis, and weakness or paralysis.
Book an Appointment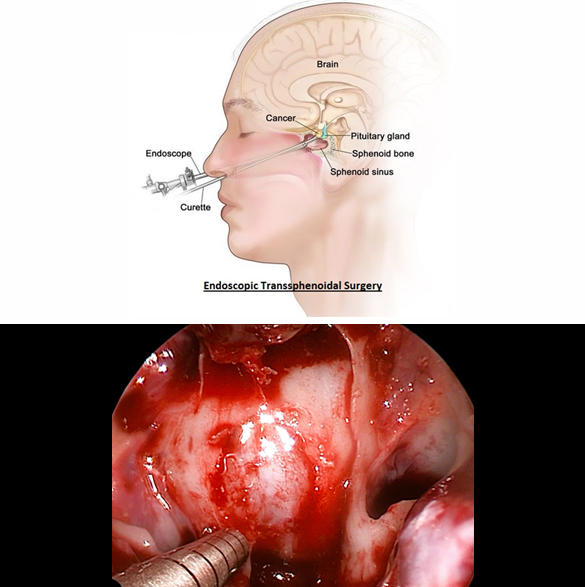
Endoscopic Transsphenoidal Surgery for Pituitary Tumor
Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery has become the gold standard for treating many pituitary tumors due to its safety and effectiveness. Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove pituitary tumors through the nasal passages and sphenoid sinus. This technique utilizes an endoscope, a thin, tube-like instrument with a camera, to visualize and access the tumor, avoiding the need for traditional incisions on the face or skull. Patients typically experience a quicker recovery and shorter hospital stay compared to traditional surgery. Few complications of this surgery may include cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak from nose, bleeding, and hormonal deficiency.
Book an Appointment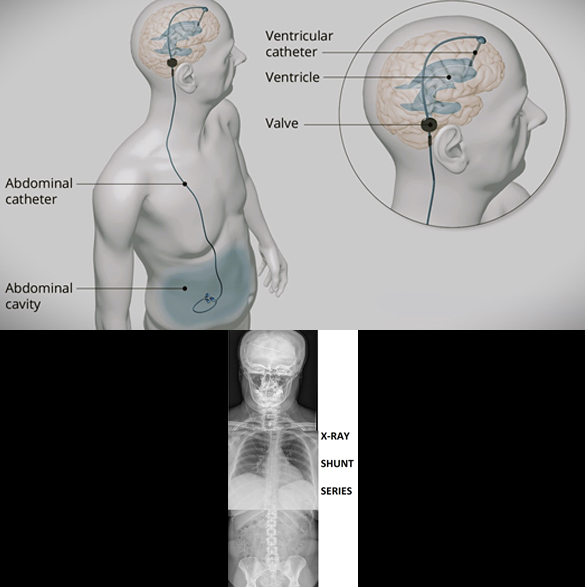
VP Shunt Procedure for Hydrocephalus
Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a type of surgical treatment for hydrocephalus. VP shunt is placement of a catheter inside the body that drain the excessive fluid (CSF) from the brain to abdomen where it is absorbed, creating an artificial pathway to control CSF volume. VP shunt placement is one of the common procedures in neurosurgery. VP shunts are generally placed for life with a few exceptions. There are many types of VP shunts available depending on the quality (Medtronic, Integra, etc.) and functionality (fixed pressure, programmable). There are some other shunts than can also be performed for hydrocephalus; Lumboperitoneal (LP shunt), Ventriculoatrial (VA shunt), Ventriculopleural (VPl shunt). A few complications of the shunt surgery may be infection, shunt blockage, and over-drainage.
Book an Appointment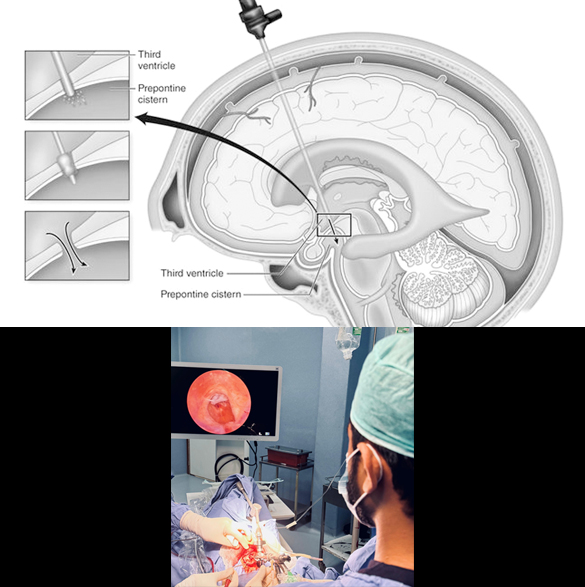
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy for Hydrocephalus
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) is another type of surgical treatment for hydrocephalus where a neurosurgeon inserts an endoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) through a small hole in the skull and into the brain's ventricles. It creates a diversion in the pathway of fluid (CSF) in the brain, with the help of an endoscope. ETV can prevent from placing a permanent catheter (VP shunt) in the brain. ETV is generally an elective procedure and can only be performed in some specific cases of hydrocephalus. It is usually avoided in emergency cases but can be performed even in infections. While ETV is a successful procedure for many, the success rate can vary depending on the cause of hydrocephalus and the patient's individual circumstances. Complications of this surgery may include wound infection, intracranial bleeding (failure to complete the procedure), and postoperative increasing hydrocephalus.
Book an Appointment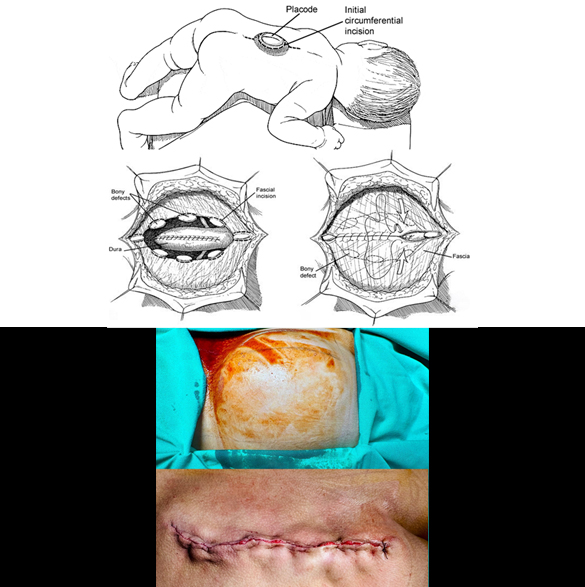
Spina Bifida Surgery
Spina bifida surgery is performed as an open surgical procedure under microscope or surgical loupes. This surgery involves reconstruction of the vertebral column, closing the open congenital defect. The goal of the surgery include prevention of infection, protection of spinal cord and addressing potential complications. Spina bifida surgery should be performed as early as possible after its diagnosis. Early surgery shows better outcome with less complications. While surgery can repair the defect, it cannot reverse nerve damage that has already occurred. Associated problems like hydrocephalus may require detailed investigations prior to surgery. Few complications of the surgery may be wound infection, hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, and weakness or paralysis.
Book an Appointment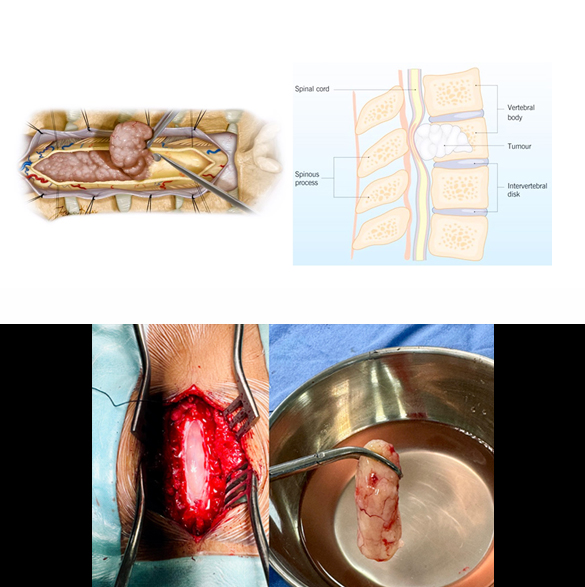
Spinal Tumors Excision
Surgical excision (removal) is generally required for all kind of spinal tumors. Most procedures for spinal tumor excision require opening up spine at the back and then removal. These procedures may require spinal instrumentation (fixation with screws and rods) in some cases. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible, potentially curing some benign tumors, or to alleviate symptoms like pain and nerve compression in others. Surgical approaches vary depending on tumor type and location, and may involve techniques like en-bloc resection (removing the tumor in one piece) or more targeted removal of the tumor tissue. Complications of the surgery may includewound infection, bleeding, recurrence, and weakness or paralysis.
Book an Appointment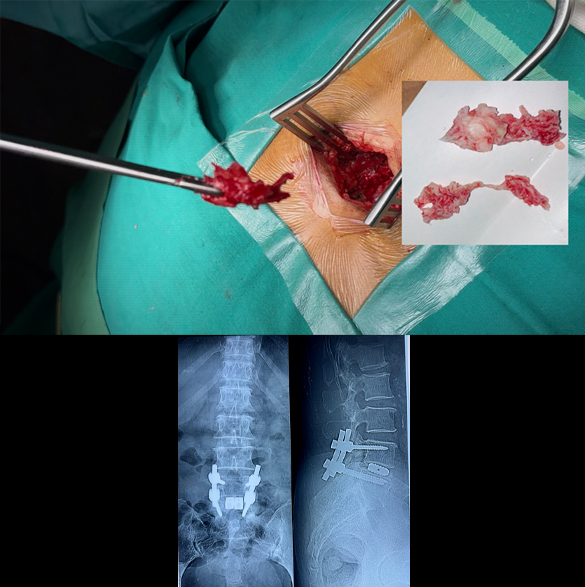
Spinal Disc Prolapse Surgery (Open, Micro-endoscopic & Endoscopic Surgery, TLIF/PLIF)
There are multiple surgical options for treatment of spinal disc prolapse. Commonest are Open discectomy or microdiscectomy. Other options are micro-endoscopic, and pure endoscopic. Not all patients can be treated with endoscopy; smaller unilateral disc prolapse is one of the indication. Some patients with spine alignment issues may require spinal instrumentation (fixation with screws and rods) during disc removal surgery. Similarly disc replacement surgery (TLIF/PLIF) is also an option in fully active middle age patients. Generally, the outcome of disc prolapse surgery is good and patients is mobilized on the same day while full recovery can take 2 to 4 weeks time. A few complications of the surgery may be wound infection, bleeding, postoperative muscle spasm, and nerve damage (rare and usually temporary).
Book an Appointment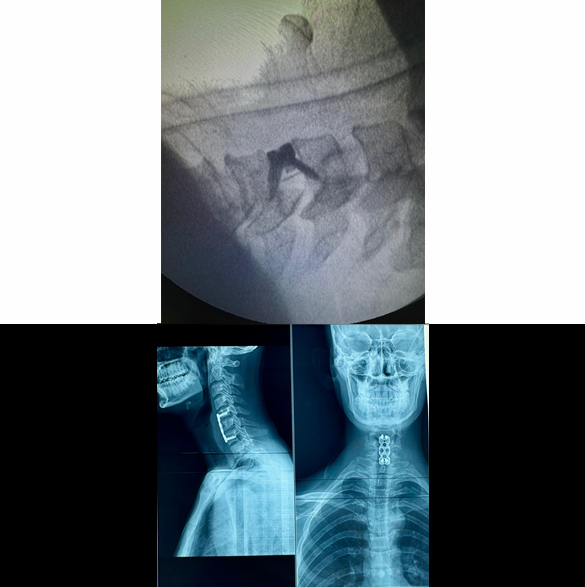
Cervical Disc Prolapse Surgery
Cervical disc prolapse surgery is performed to treat symptomatic cervical disc disease, by fusing the two segments as in traditional anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) or by replacing the diseased disc with an artificial disc (also called cage). Sometimes, another procedure called anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion (ACCF) may be needed if two disc prolapse is present at two adjacent levels. Nowadays, cervical disc replacement surgery, also called Cervical Arthroplasty, is more frequently performed with better outcomes and even if disc prolapse is present at more than one level. Few complications of this surgery may be wound infection, bleeding, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, and nerve damage (rare and usually temporary).
Book an Appointment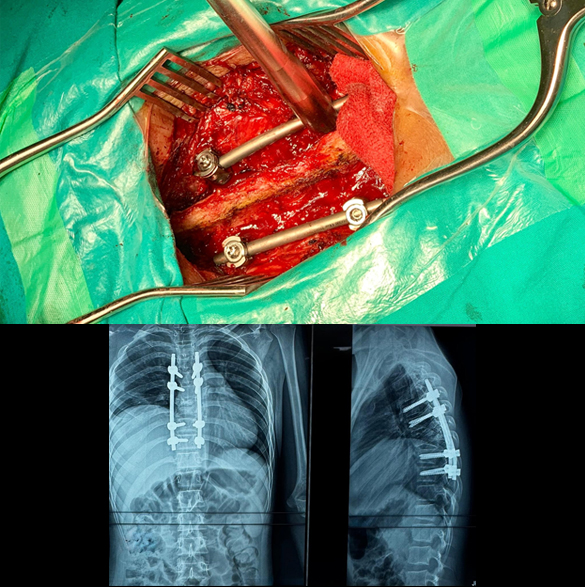
Spinal Fracture Fixation/Fusion (Open and Minimal Invasive Surgery)
Spinal fractures generally require spinal instrumentation (fixation with screws and rods) in most cases, to main the spinal alignment and future complications like paralysis and kyphosis. These procedures usually require opening of the spine at back and placing screws and rods at multiple vertebrae. Early surgery is a key in the outcome of spinal fractures, because delaying the surgery patient may develop paralysis (weakness in power of limbs). New techniques like minimal invasive surgery (MIS) where large skin incision is not used, can also be performed in some patients. Complications of fixation/fusion surgery may include wound infection, bleeding, and implants/screws improper placement.
Book an Appointment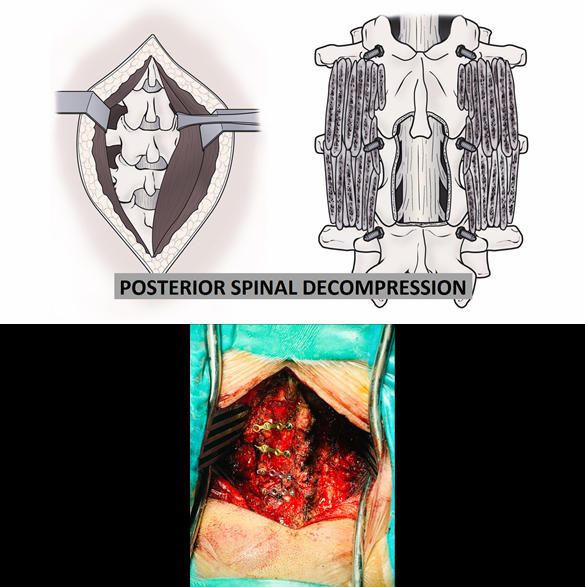
Spinal Stenosis Surgery (Posterior Spinal Decompression, Laminoplasty)
Posterior spinal decompression surgery for spinal stenosis is similar to disc surgery where the surgery is usually performed with an incision at the back. The outcome of spinal stenosis surgery is good if diagnosed and performed early. Delaying the surgery may cause complete paralysis or severe difficulty in walking and outcome will not be so good and improvement may take long time. Sometimes, patient may require instrumentation (fixation with screws and rods) especially old age patient with cervical spine stenosis at multiple vertebral levels. Few complications of posterior spinal decompression may be wound infection, bleeding, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak, and nerve damage (rare and usually temporary).
Book an Appointment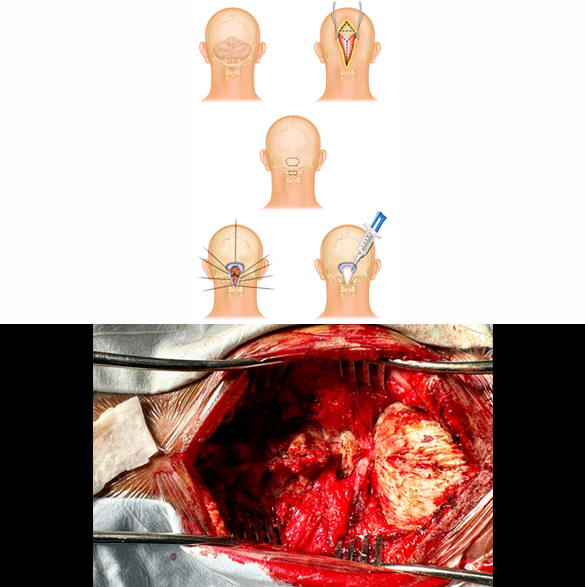
Chiari Malformation Surgery
Surgery for Chiari malformation has three options with different indications:
- Posterior suboccipital decompression (which may include C1 laminectomy)
- Posterior suboccipital decompression + Duraplasty
- Posterior suboccipital + Duraplasty + Tonsillar cauterization
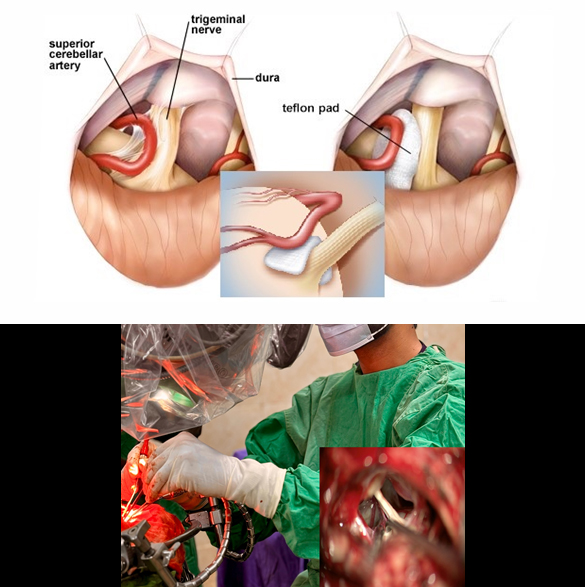
Trigeminal Neuralgia Treatment (Percutaneous Injection, Microvascular Decompression Surgery)
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) can be divided as:
- Pain medications
- Percutaneous injection, Rhizotomy
- Microvascular decompression (MVD)
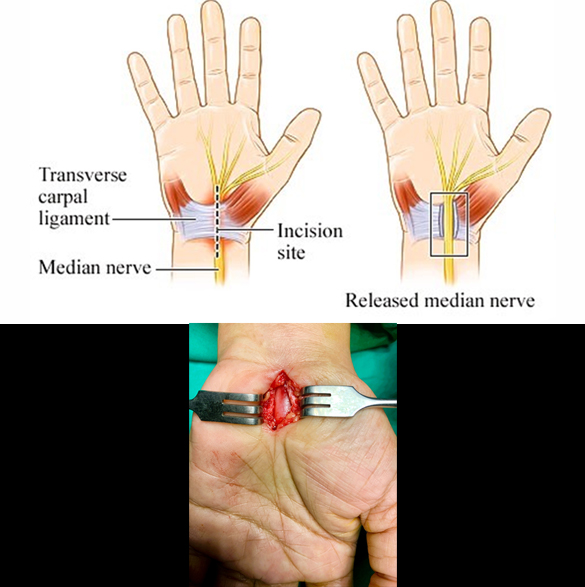
Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel release surgery is a procedure to relieve pressure on the median nerve in the wrist, which is compressed in carpal tunnel syndrome. It involves cutting the transverse carpal ligament which forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, with a small incision at the wrist, to create more space for the nerve. The surgery is usually performed as a day case procedure under local anesthesia making the hand numb during the surgery. The outcome of surgery is very good when performed for the right indication after a proper clinical examination and investigation. Few complications of the carpal tunnel release surgery can be infection and recurrence of symptoms.
Book an Appointment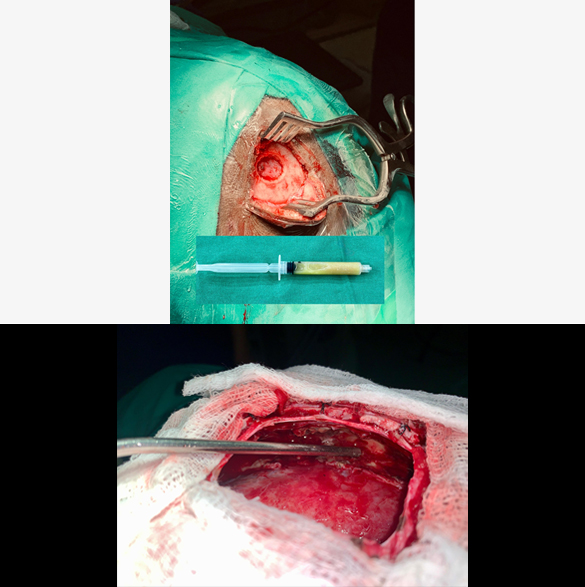
Brain Abscess Surgery
Brain Abscess Treatment involves a combination of emergency medical care, neurosurgical intervention, and long-term antibiotic therapy. Brain abscess is a serious medical emergency, having a potential risk of serious complications of seizures, meningitis, brain hemorrhage, paralysis, and even death. Antibiotics are usually started at suspicion of a brain abscess and given through oral or intravenous route for 6 to 12 weeks. Surgical treatment options include Burr-hole (creating a small hole in skull) drainage/aspiration and Craniotomy (opening up the skull bone and aiming to excise the abscess completely). Complications of this surgery may include bleeding, recurrence, and paralysis.
Book an Appointment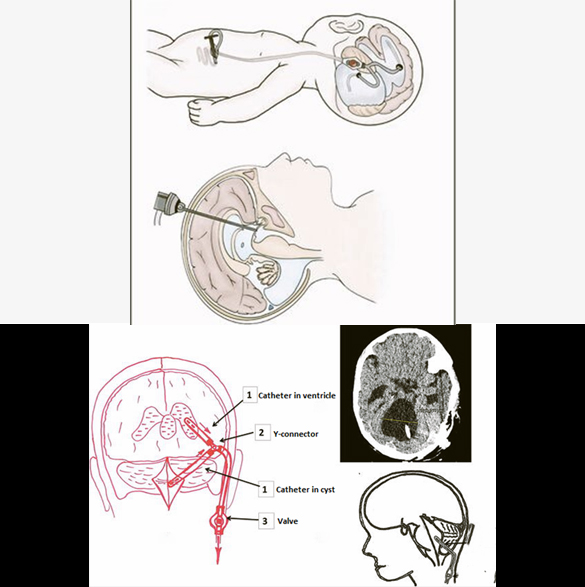
Dandy-Walker Malformation Surgery
Dandy-Walker Malformation treatment is focused on managing the associated hydrocephalus and controlling the increasing intracranial pressure to improve the developmental and neurological outcomes. The Dandy-Walker malformation related hydrocephalus is treated with a Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt same as for a usual case of hydrocephalus, with or without the need of shunting the enlarged cyst (Cystoperitoneal shunt) in the posterior part of the brain. Sometimes, cystoperitoneal shunt is the only surgery that patient needs. Endoscopic fenestration may be helpful in a few cases, avoiding any shunt placement. Complications of the surgery are mainly shunt related like infection, blockage, or slippage/migration of shunt.
Book an Appointment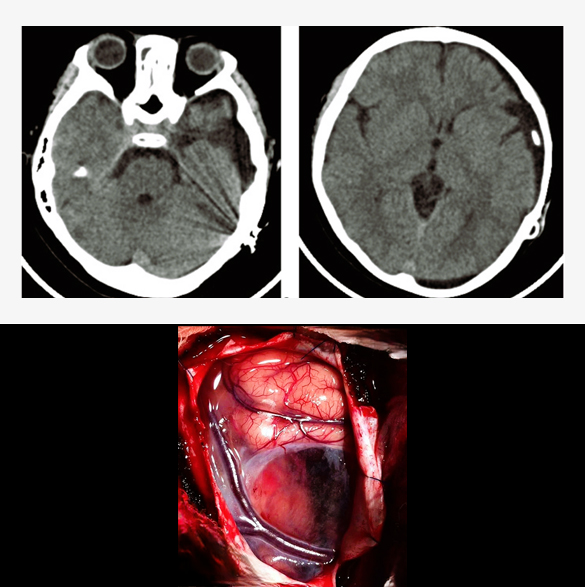
Arachnoid Cyst surgery
Most patients with arachnoid cyst asymptomatic and require no intervention, surgery is indicated when they cause symptoms due to mass effect or progressive enlargement, hydrocephalus, uncontrolled seizures, visual problems, or paralysis. Surgical treatment options include Cystoperitoneal shunt, Endoscopic fenestration and Microsurgical fenestration. Cystoperitoneal shunt is a common and simpler treatment similar to ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS), placing a tube to drain the cyst fluid into the peritoneum (abdomen). Fenestration creates a new connection within the brain, draining the fluid through it. A few complications of the surgery may be shunt blockage, infection, and bleeding.
Book an Appointment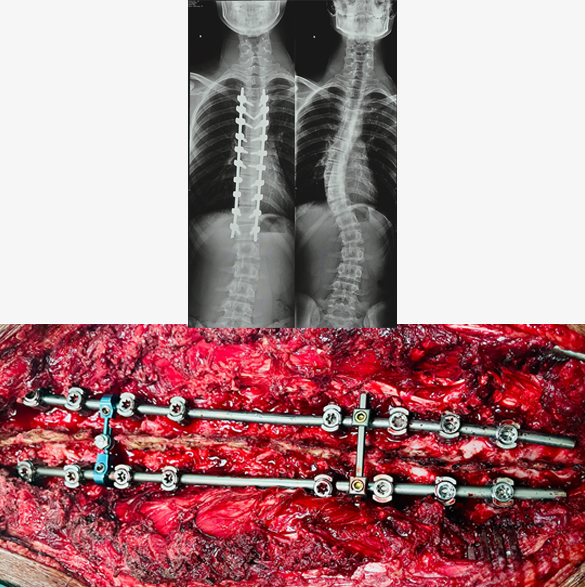
Deformity Surgery for Scoliosis
Scoliosis reconstructive surgery, primarily spinal fusion with instrumentation, aims to correct spinal curvature by fusing vertebrae together and stabilizing the spine with metal rods and screws. This procedure is often recommended for severe scoliosis cases, particularly when the curve exceeds 40 degrees or moderate scoliosis where patient has severe symptoms. Deformity surgery is a type of complex spinal procedure where the surgery time is long and require an extensive investigations prior to surgery. While generally successful, it's a major surgery with potential short-term and long-term effects. Complications of this surgery may include infection, bleeding, weakness or paralysis, and screw/rod misplacement.
Book an Appointment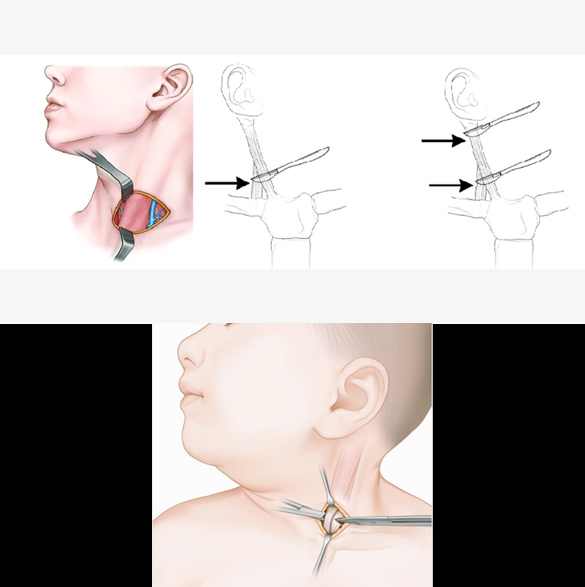
Torticollis Surgery
Surgery is indicated for torticollis when the if conservative treatments (e.g., medicine and physiotherapy) fail after 6–12 months, persistent head tilt beyond 1 year of age, significant asymmetry of the face or skull (plagiocephaly), limited neck range of motion, and cosmetic or psychosocial concerns in older children/adolescents. Surgery involves the Sternocleidomastoid muscle release (detaching the muscle at one or both ends) or lengthening. Postoperative collar, physiotherapy and rehabilitation is generally needed in these patients. A few complications of this surgery may be recurrence of the contracture, or scar formation.
Book an Appointment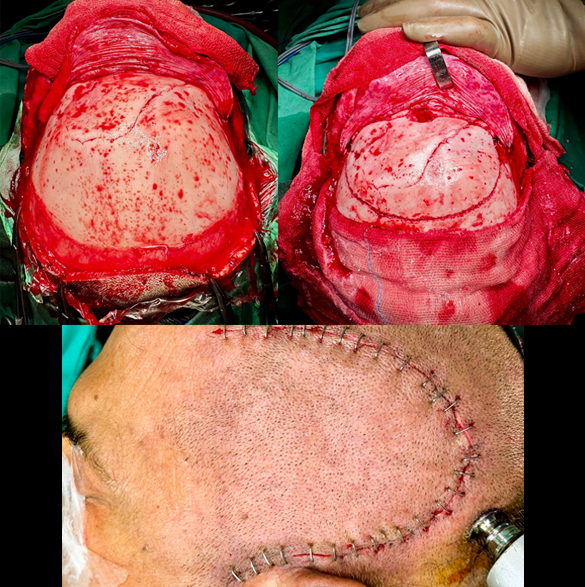
Head Trauma Surgery
Surgery in case of a head trauma is performed when there is intracranial hematoma (blood) of significant amount or depressed skull fracture causing pressure on the normal brain. This life-threatening condition necessitates emergency surgery in a well-equipped environment, often requiring postoperative intensive care unit (ICU) admission. Surgery, called craniotomy, is performed to open up the skull and remove the hematoma or reposition the depressed skull bone. Sometimes, a part of skull bone is removed (called decompressive craniectomy) to control the intracranial pressure, requiring a second surgery to replace the bone, months later after complete recovery. Complications of the surgery can be rebleeding, infection, hydrocephalus, seizures, paralysis, coma or even death in severe case.
Book an Appointment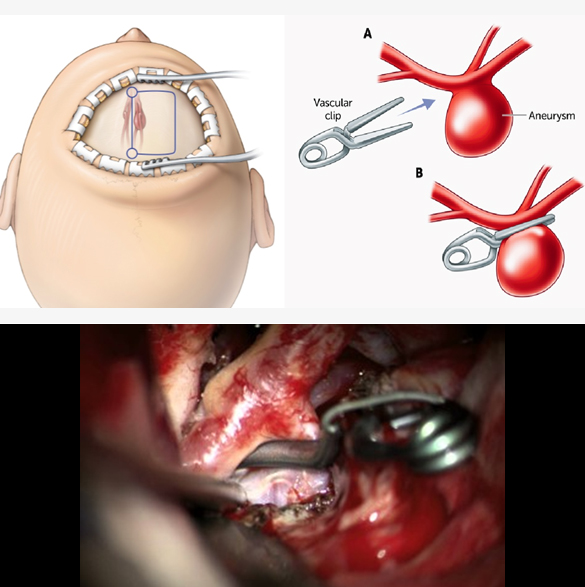
Aneurysm Clipping
Aneurysm clipping is a microsurgical procedure used to treat intracranial (brain) aneurysms, blocking the flow of blood into the bulb of aneurysm and preventing future risk of rupture. Common indication of the clipping are ruptured aneurysm, large size or progressively enlarging, irregular shape, causing any neurological deficit. CT angiography (CTA) or Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is usually performed before surgery to know the location, size and detailed anatomy. Craniotomy is performed, and with the help of microsurgical dissection reaching the aneurysm to clip it with titanium or stainless-steel clip. Postoperative care is needed in an intensive care unit (ICU) for monitoring and serial clinical assessment. Complications of aneurysm clipping may include infection, bleeding, vasospasm, seizure, hydrocephalus and neurological deficit. Endovascular coiling is an alternate to aneurysm clipping in some particular cases.
Book an Appointment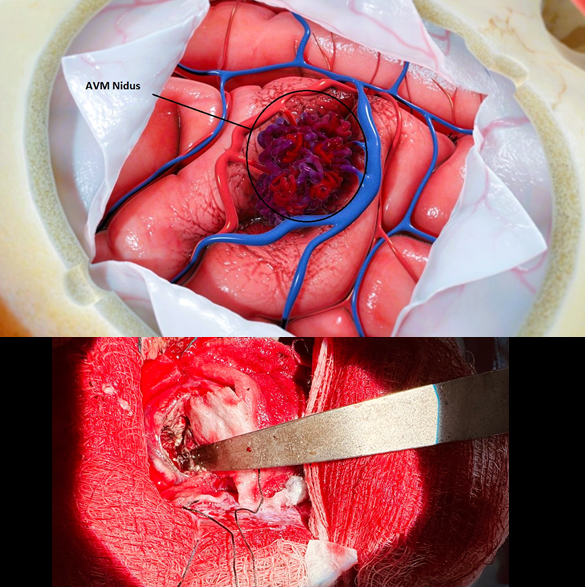
Cerebral AVM Surgery
Cerebral AVM surgery is aimed at removing an abnormal tangle of arteries and veins in the brain that bypasses the normal capillary system. Surgical resection is often performed to prevent hemorrhage, eliminate seizures, or relieve other neurological symptoms caused by the AVM. Detailed MRI/MRA and Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) is done before the surgery. Craniotomy is performed, and with the help of microsurgical dissection isolate and disconnect arterial feeders, preserving the normal brain tissue. Postoperative care is generally needed in an intensive care unit (ICU) for monitoring and serial clinical assessment. Complications of AVM surgery may include infection, bleeding, seizure, stroke and neurological deficit. Other treatment options like Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Endovascular Embolization can also be used in some specific cases.
Book an Appointment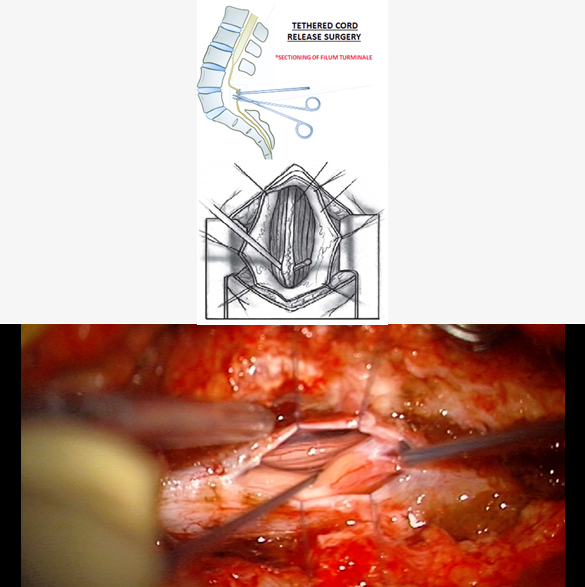
Tethered Cord Release Surgery
Surgical tethered cord release is the primary treatment to relieve spinal cord tension and prevent further neurological deterioration in tethered cord syndrome (TCS). Surgery is performed with there is neurological symptoms (leg weakness, gait issues), bladder or bowel dysfunction, and progressive scoliosis or foot deformities. Surgery is performed after clinical and radiological assessment. Midline incision is given over the spine, performing the laminectomy at one or more levels, opening up the dura and then sectioning the Filum terminale with dissection of other adhesions. A few complications of this surgery may be infection, CSF leak, neurological worsening (weakness or bladder dysfunction)and retethering.
Book an Appointment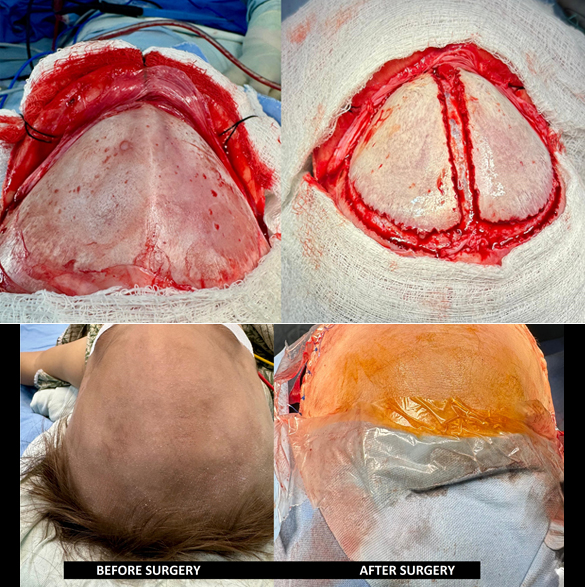
Craniosynostosis Surgery (Strip Craniectomy or Reconstructive Cranioplasty)
Surgery is performed for Cranisynostosis, to correct skull shape, relieve any intracranial pressure, and allow normal brain development. Ideal age for this surgery is 3 to 6 months age of the baby, may be helpful up to 12 months of age in some case. Earlier surgery leads to better cosmetic and developmental outcomes. The goal is to open up the fused/closed sutures, reconstruct the skull shape (improve cosmetical appearance) and relieve pressure and improve the neural development of the child. Surgery may be performed as traditional open surgery or endoscopically, depending on the type of craniosynostosis, symptoms, age of the child. Some cases also require a craniofacial reconstruction (of orbit and facial bones), where maxillofacial surgeon is also engaged. A few complications of the surgery may include bleeding, infection, CSF leak, and bone deformity.
Book an Appointment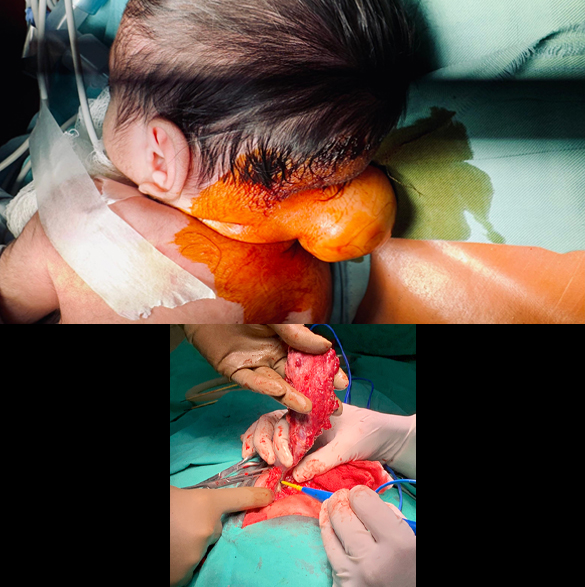
Encephalocele Repair
Surgery is the definitive treatment for Encephalocele and it aims to repair the skull defect, remove nonviable (nonfunctional) brain tissue, and preserve neurologic function. Surgery is ideally performed at the earliest after diagnosis (usually) at birth to prevent further herniation (bulging out of contents) and risk of rupture or CSF leak. Generally preoperative CT or MRI is needed to assess contents of the sac, evaluate venous sinuses or vascular involvement, and assess for hydrocephalus or other anomalies. Surgery involves the skin incision, carefully dissecting out the herniated contents and then proper closure of the dura and skin. A few complications of encephalocele repair surgery may include CSF leak, bleeding, infection, and hydrocephalus.
Book an Appointment